Caixa Econômica Federal, Correios, Embrapa, BNDES and USP are examples of public enterprises. Mixed-economy companies are enterprises with the majority of stocks owned by the government, but that also have stocks owned by the private sector and usually have their shares traded on stock exchanges.
What are types of public enterprises?
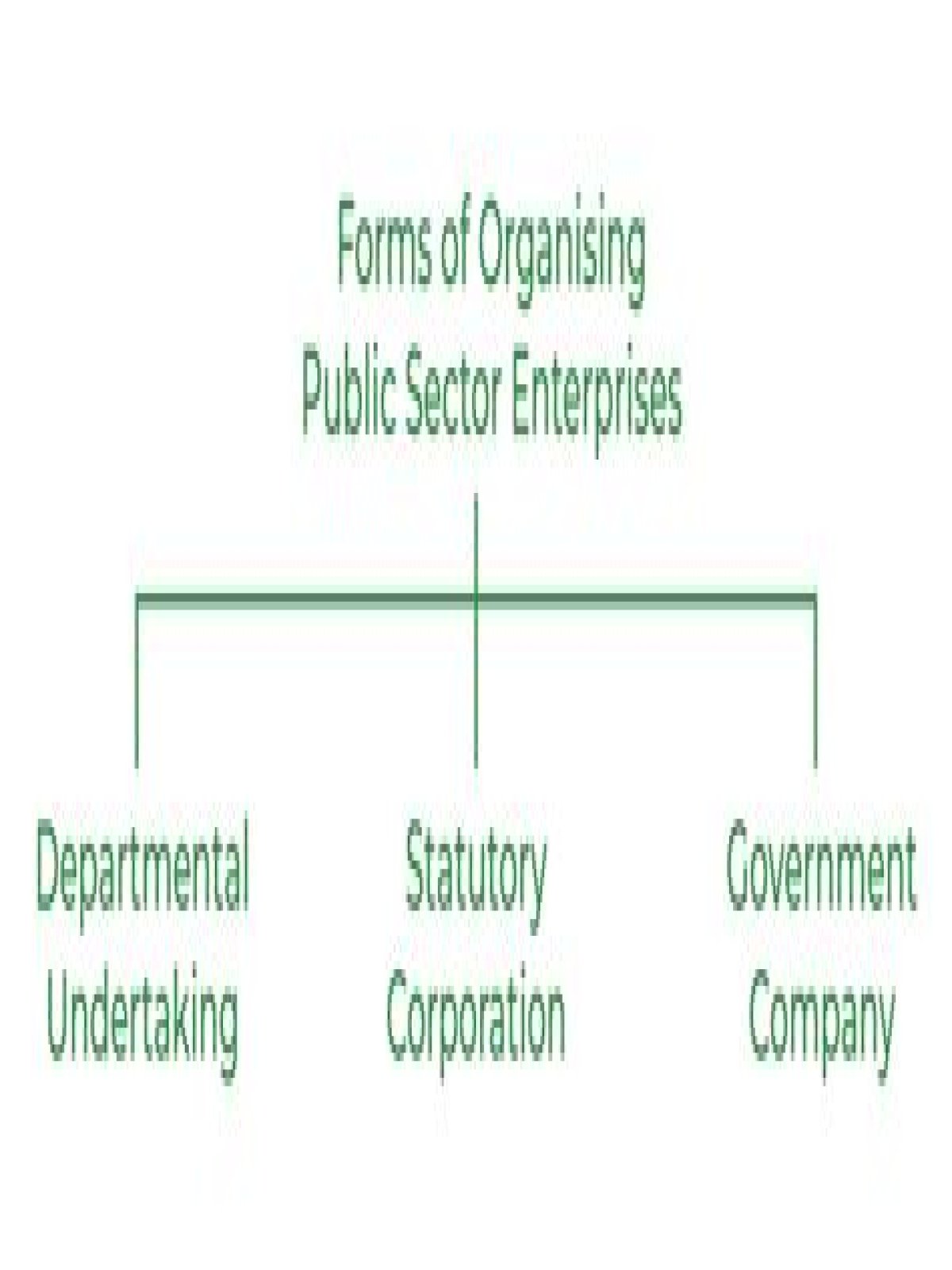
Public enterprises can be of three types as follows:
- Departmental Undertaking. It is created by government. It is part of the government system and is attached as department to a government ministry. Department undertaking has no separate legal status.
- Public Corporation.
- Government Company.
What are the characteristics of public enterprise?
CHARACTERISTICS OF PUBLIC ENTERPRISES
- They are state owned.
- It is created by specific government status, it may be by edit or by law.
- It is subject to company law, but only the company type.
- It has a legal personality.
- It can sue or be sued.
- It is finance differently from others.
- It can generate it funds from either by shares.
How do public enterprises work?
Characteristics of Public Enterprises They function under the direct control of the government and some are even established under statutes and Companies Act. Therefore, public enterprises are autonomous or Semi-Autonomous in nature. Therefore, the public sector enterprises enjoy a monopoly in operation.
What is another name for public enterprise?
A government-owned corporation, state-owned company, state-owned entity, state enterprise, publicly owned corporation, government business enterprise, commercial government agency, public sector undertaking or parastatal is a legal entity created by a government to undertake commercial activities on behalf of an owner …
What is the role of public enterprise?
Public enterprise, a business organization wholly or partly owned by the state and controlled through a public authority. Some public enterprises are placed under public ownership because, for social reasons, it is thought the service or product should be provided by a state monopoly.
Table of ContentsWhat are the role of public enterprises?
Public enterprises in Nigeria were established to propel socio-economic development and to guard against the control of the economy from foreign domination and exploitation. This accounts for why a larger proportion of the national budget has been voted for the creation and sustenance of public enterprises.
What is the advantages of public enterprise?
Advantages of Public Enterprises. Charges low prices. Provide essential facilities like education, health, free or at reduced prices. Ensures efficient control of industry.
Who owns the public enterprises?
The term public enterprise denotes a form of business organisation owned and managed by the government or any other public authority. So it is an undertaking owned and controlled by the local or state or central government.
What is public enterprise Wikipedia?
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia. A government-owned enterprise in India is called a Public Sector Undertaking (PSU) or a Public Sector Enterprise. These companies are wholly or partly owned by the Government of India or one of the many state or territorial governments or both together in parts.
What is meant by statutory corporation?
A statutory company definition is defined as a company that is created by a Special Act of the Parliament. It is a company that provides services of value to the public.
Why do we need public enterprises?
Public enterprises are important source of government revenue. They pay various types of taxes, such as customs duties, value added tax, excise duty, income tax and others. Such taxes are important in government revenue. Profit generated by public enterprises can be used to fund development programs.
What are the main objectives of public enterprises?
What are the Objectives of Public Enterprises?
- Economic development: Public enterprises were set up to accelerate the rate of economic growth in a planned manner.
- Self-reliance:
- Development of backward Areas:
- Employment generation:
- Economic surplus:
- Egalitarian society:
- Consumer welfare:
- Public utilities:
Are public enterprises owned by public?
What are the advantages of public enterprises?
Advantages of a Public Corporation
- Economies of scale.
- Easier planning and coordination.
- Autonomous set-up.
- Protection of public interest.
- Quicker decisions.
- Raising funds through private sourcing.
What are statutory corporations give an example?
Reserve Bank of India, State Bank of India, Life Insurance Corporation, Unit Trust of India, Employees State Insurance Corporation, Oil and Natural Gas Corporation etc. are some examples of statutory corporations.
What are examples of government corporations?
Appendix. Federal Government Corporations
- Commodity Credit Corporation. (15 U.S.C. 714)
- Export-Import Bank. (12 U.S.C. 635)
- Federal Crop Insurance Corporation.
- Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation.
- Federal Financing Bank.
- Federal Prison Industries (UNICOR)
- Financing Corporation.
- Government National Mortgage Corporation.
What is the role of public enterprises?
Here we detail about the following nine important roles played by public sector in Indian economy, i.e., (1) Generation of Income, (2) Capital Formation, (3) Employment, (4) Infrastructure, (5) Strong Industrial Base, (6) Export Promotion and Import Substitution, (7) Contribution to Central Exchequer, (8) Checking …
Who own the public enterprises?
the government The term public enterprise denotes a form of business organisation owned and managed by the government or any other public authority. So it is an undertaking owned and controlled by the local or state or central government.