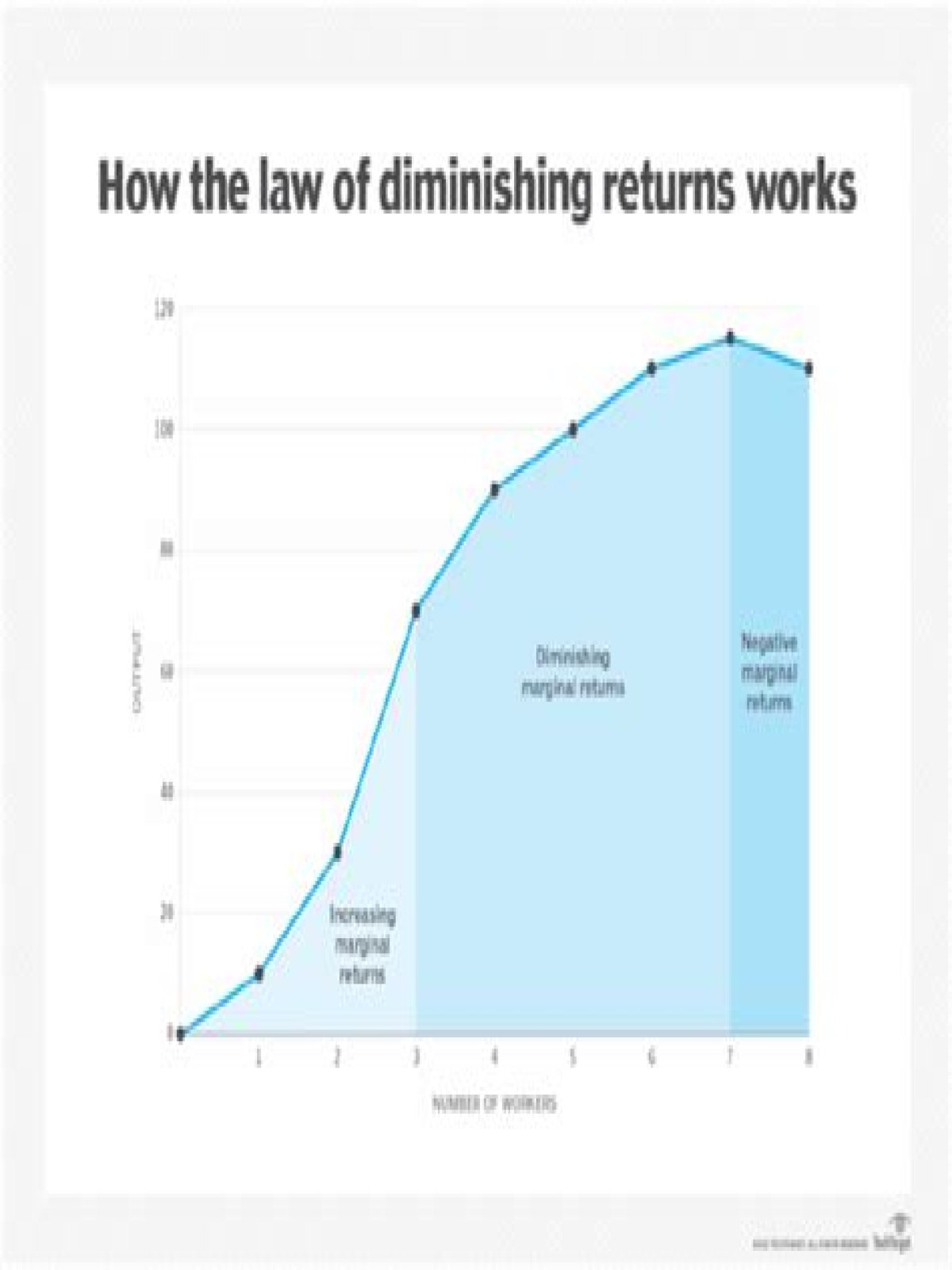
Diminishing returns, also called law of diminishing returns or principle of diminishing marginal productivity, economic law stating that if one input in the production of a commodity is increased while all other inputs are held fixed, a point will eventually be reached at which additions of the input yield …
What are the effects of diminishing marginal returns?
Diminishing marginal returns is an effect of increasing input in the short run after an optimal capacity has been reached while at least one production variable is kept constant, such as labor or capital. The law states that this increase in input will actually result in smaller increases in output.
What are the causes of diminishing returns to a factor?
The main factors that cause diminishing returns are: When a given quantity of a fixed factor is combined with successively larger amount of the variable factor, the successive units of the variable factors will get smaller and smaller share in total quantity of the fixed factor to work with them.
Is law of diminishing returns good or bad?
Why the Law of Diminishing Returns Can Be a Bad Deal This is the reason The Law of Diminishing Returns makes it so difficult to achieve mastery. It requires a lot more input over time, to see the same incremental returns on your efforts that once appeared in the beginning.
What is the law of diminishing returns explain?
The law of Diminishing Returns states that the result of adding a factor of production is a smaller increase in output. The addition of any amounts of a factor of production, after some best possible level of capacity utilization, will inevitably capitulate decreased per-unit incremental returns.
What does the law of diminishing returns mean?
The law of diminishing returns states that beyond the optimal level of capacity, every additional unit of production factor will result in a smaller increase in output while keeping the other production factors constant.
When does the law of increasing returns decline?
The law of increasing returns is also named as the Law of Diminishing Cost. When the addition to output becomes larger, as the firm adds successive units of a variable input to some fixed inputs, the per unit cost begins to decline.
When does Stage 3 of the law of diminishing returns start?
The origin of stage 3 starts from the maximum point of the TP curve. In this stage, the TP curve now starts to decline. Moreover, the MP curve becomes negative coupled with a fall in the AP curve. The excessive addition of variable inputs leads to negative returns at this stage.
Why does diminishing returns lead to higher productivity?
This is because, with a sufficient quantity of variable factor, the introduction of specialisation and division of labour becomes possible which leads to higher productivity. Throughout the stage of diminishing returns, the total product keeps on increasing.